Leak testing using the volume flow method is always applied when a component has a large permissible leak rate. This is the case, for example, with many exhaust-carrying parts in the post-catalytic converter area or with ventilation systems. With pressure measuring and gas detection methods, the measuring range is usually insufficient for such components.
Method:
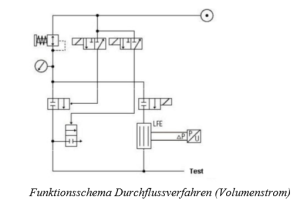
The test object is sealed, filled, and kept under constant pressure. The amount of air flowing out through the leak is replenished and measured.
For large-volume components, a filling process is connected upstream, during which the test object is filled via a bypass line.
Test medium:
Air (usually under slight positive or negative pressure)
detectable leak rates:
>100 cm³/min
Advantages
- The test is carried out under specified temporal conditions and pressure conditions. As a result, the test results are independent of the diligence of a worker and are more reproducible.
- The test results can be automatically documented.
- After calibrating the differential pressure / leak rate factor, this method enables a quantifiable leak rate determination. This allows the permissible tolerances to be exploited.
- The sensor technology is robust and very insensitive.
- The test fixtures require only a small amount of mechanical effort.
Disadvantages:
- The scaling is related to a specific test pressure. If a different pressure is used, a different calibration or conversion of the measured values is required.
- With strong temperature changes during the measuring time, the measured values can be influenced.
Notes:
- Above all, exact pressure regulation is very important during the measuring time.
- The measurement is carried out as a differential pressure measurement via a laminar flow element. This means that the flow velocity essentially determines the measured value.
- When using it, it should be noted that the medium under test pressure is measured and that flow testing devices using the volume flow method are usually scaled to a specific test pressure.


