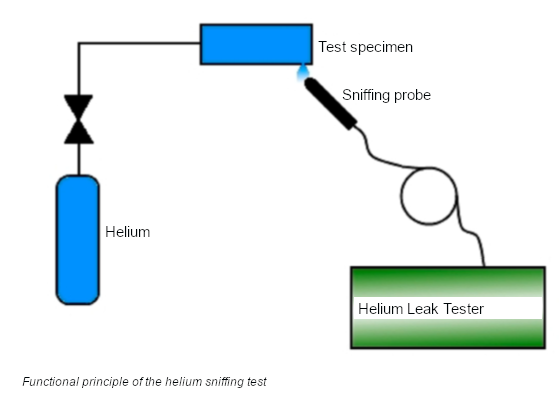
Method:
The test object is sealed, filled with helium, and examined on the surface for traces of helium escaping from a leak using a usually hand-guided sniffing probe.
For this purpose, the gas mixture at the tip of the probe is sucked into the helium leak detector and examined for traces of helium using a mass spectrometer.
Test medium:
Helium (pure or in any mixing ratios with other gases)
detectable leak rates:
>0.00001 cm³/min
Advantages
- Very small leaks can be detected.
- The test method is simple to use.
- The temperature and elasticity of the test object have no influence on the test result.
- A leak can be easily located with the hand-held sniffing probe.
Disadvantages:
- The natural helium content of 5 ppm in the atmosphere represents the detection limit for traces of test gas escaping from a leak.
- Often unsuitable for testing plastic parts due to the permeation of helium in certain plastics.
- The test gas escapes from a leak in the form of a cloud. The measurement of the gas concentration as a measure of the leak rate is strongly determined by the position of the measuring point (sniffing probe) to the leak. A quantitative leak rate determination is therefore extremely difficult with manual guidance of the sniffing probe.
- As a result, the automatic documentation of the test results is almost impossible.
- When testing with helium, there is the greatest risk of background enrichment in the workplace of all test gas methods.
Notes:
- Care must be taken to ensure that the test chamber is sufficiently and completely filled with the test gas. The test chamber should therefore be sufficiently flushed or first evacuated and then filled with the test gas.
- When testing with helium, it is particularly important that the test gas is carefully removed from the workplace after testing, as otherwise a background concentration may develop over time, which hinders or makes work impossible. Helium is the most critical of the known test gases in terms of contamination problems.