The Boyle-Mariotte Law
The Boyle-Mariotte Law, also known as Boyle’s Law, states that the pressure of ideal gases is inversely proportional to their volume at constant temperature and amount of substance. If the pressure on a gas volume is increased, its volume is reduced by the increased pressure. If the pressure is reduced, it expands.
Mathematically, Boyle’s Law is expressed by the formula:
(Approximate formula without considering temperature)
p • V = constant
therefore
p₁ • V₁ = p₂ • V₂
or
p₁/p₂ = V₂/ V₁
where
p₁: initial pressure
V₁: initial volume
p₂: final pressure
V₂: final volume
You can learn how this effect can be used to convert the pressure change in a leak test to the leak rate
Based on the above, the formula for converting flow / pressure change is derived:
(without considering temperature):
pstart • Vstart = pend • Vend + pleak • Vleak
Since Vstart = Vend = VDUT + VSystem = VTest
and pleak = 1 bar (ambient pressure), it follows:
VTest • (pstart – pend) = Vleak • 1 bar
⇒ Vleak = (VTest • Δp) / 1 bar
Normalization to flow rate (with test time):
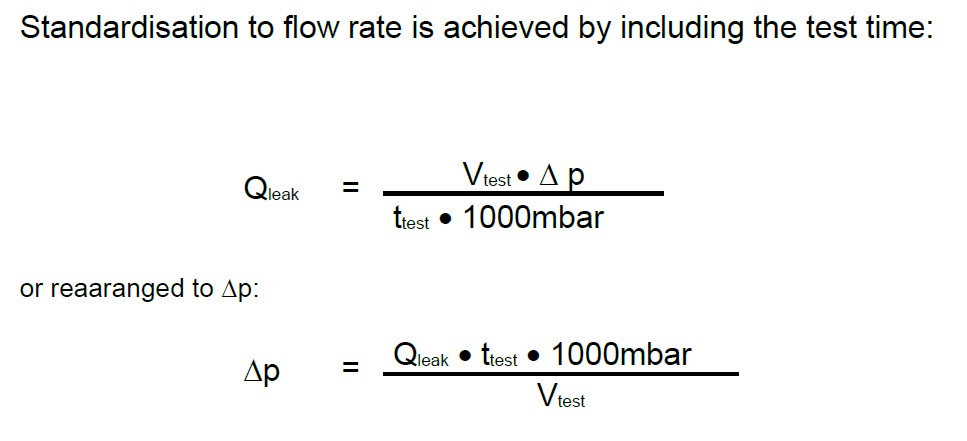
In summary, how this effect can be used to convert the pressure change in a leak test to the leak rate is explained >here<.


